That’s not how that works at all, we’ve been launching shit into space for decades now and tons of it returns, these sats from starlink are not magically going to create more than what the natual amount is showing up via meteoroids are. On top of that their estimates have a huge deviation, 800 vs 3200 is not exactly accurate.
That’s not how what works? Lumps of rock of varied composition burning up aren’t going to produce the same effects, gram for gram, as lumps of a majority of high-purity aluminium. There is little evidence that meteorites produce specifically high levels of aluminium oxide particles when entering the atmosphere (at least that I can find, I’m not dogmatic about this, I just can’t find any actual evidence that disproves this idea. I wouldn’t mind being wrong!)
Even the base estimates seem to suggest that the AlO particles will remain in the upper atmosphere for decades. AlO is proven to be a catalyst for ozone depletion, there’s quite a lot of research about that in relation to rocket exhaust gas.
The numbers of launches, satellites, and deorbits are rising pretty rapidly, so “launching shit for decades” doesn’t really mean as much as you think -
That’s not how that works at all, we’ve been launching shit into space for decades now and tons of it returns, these sats from starlink are not magically going to create more than what the natual amount is showing up via meteoroids are. On top of that their estimates have a huge deviation, 800 vs 3200 is not exactly accurate.
That’s not how what works? Lumps of rock of varied composition burning up aren’t going to produce the same effects, gram for gram, as lumps of a majority of high-purity aluminium. There is little evidence that meteorites produce specifically high levels of aluminium oxide particles when entering the atmosphere (at least that I can find, I’m not dogmatic about this, I just can’t find any actual evidence that disproves this idea. I wouldn’t mind being wrong!) Even the base estimates seem to suggest that the AlO particles will remain in the upper atmosphere for decades. AlO is proven to be a catalyst for ozone depletion, there’s quite a lot of research about that in relation to rocket exhaust gas.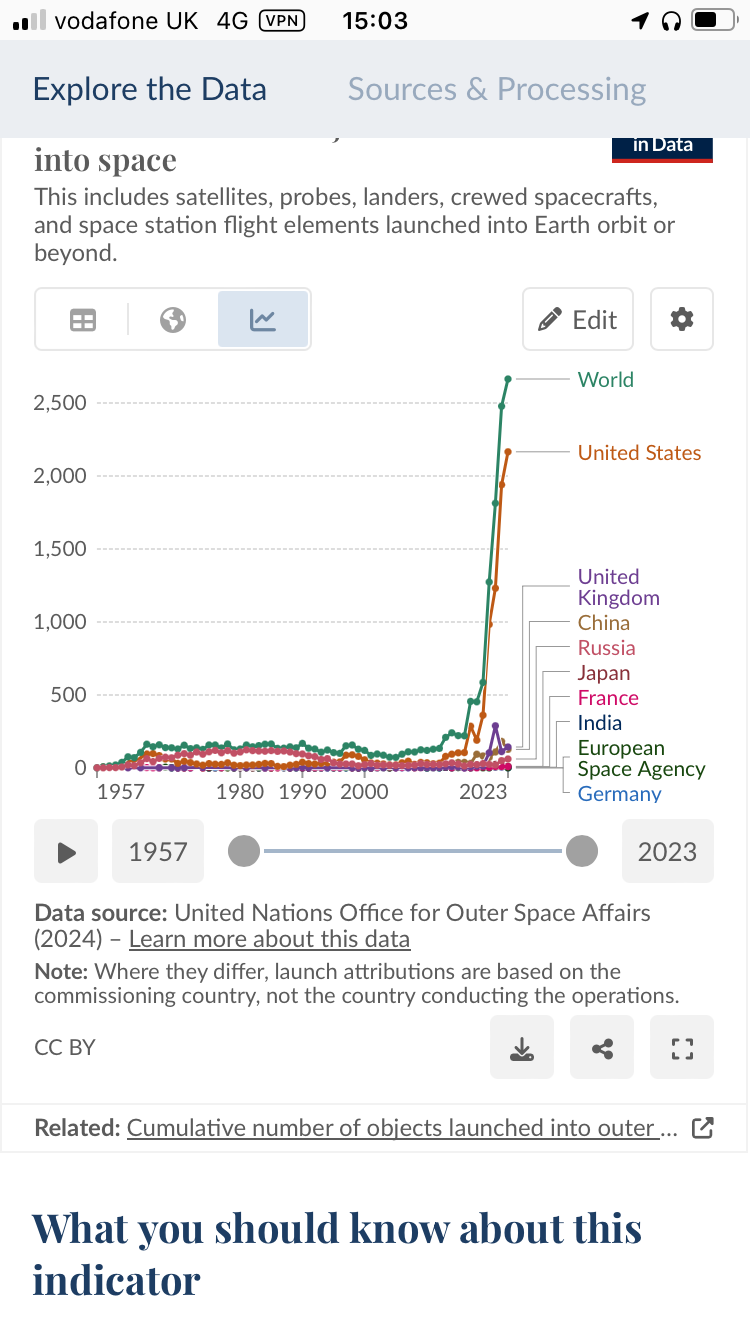
The numbers of launches, satellites, and deorbits are rising pretty rapidly, so “launching shit for decades” doesn’t really mean as much as you think -
I was pulling the number from your own paper you presented…so is your paper wrong then?