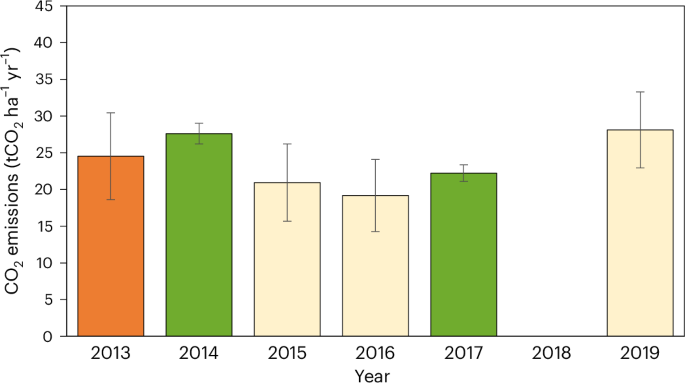
Cultivation of maize for biomethane production has expanded rapidly, including on drained peat soils. The resulting soil CO2 emissions at the point of feedstock production are largely overlooked when assessing biogas climate mitigation potential. On the basis of field-scale flux measurements, we calculate that soil CO2 emissions from biomethane feedstock production on drained peat exceed embodied emissions for an equivalent amount of natural gas by up to a factor of three.
You must log in or register to comment.