Who keeps deflecting them?!
I BELIEVE IN THE JOBS THE ASTEROID WILL CREATE
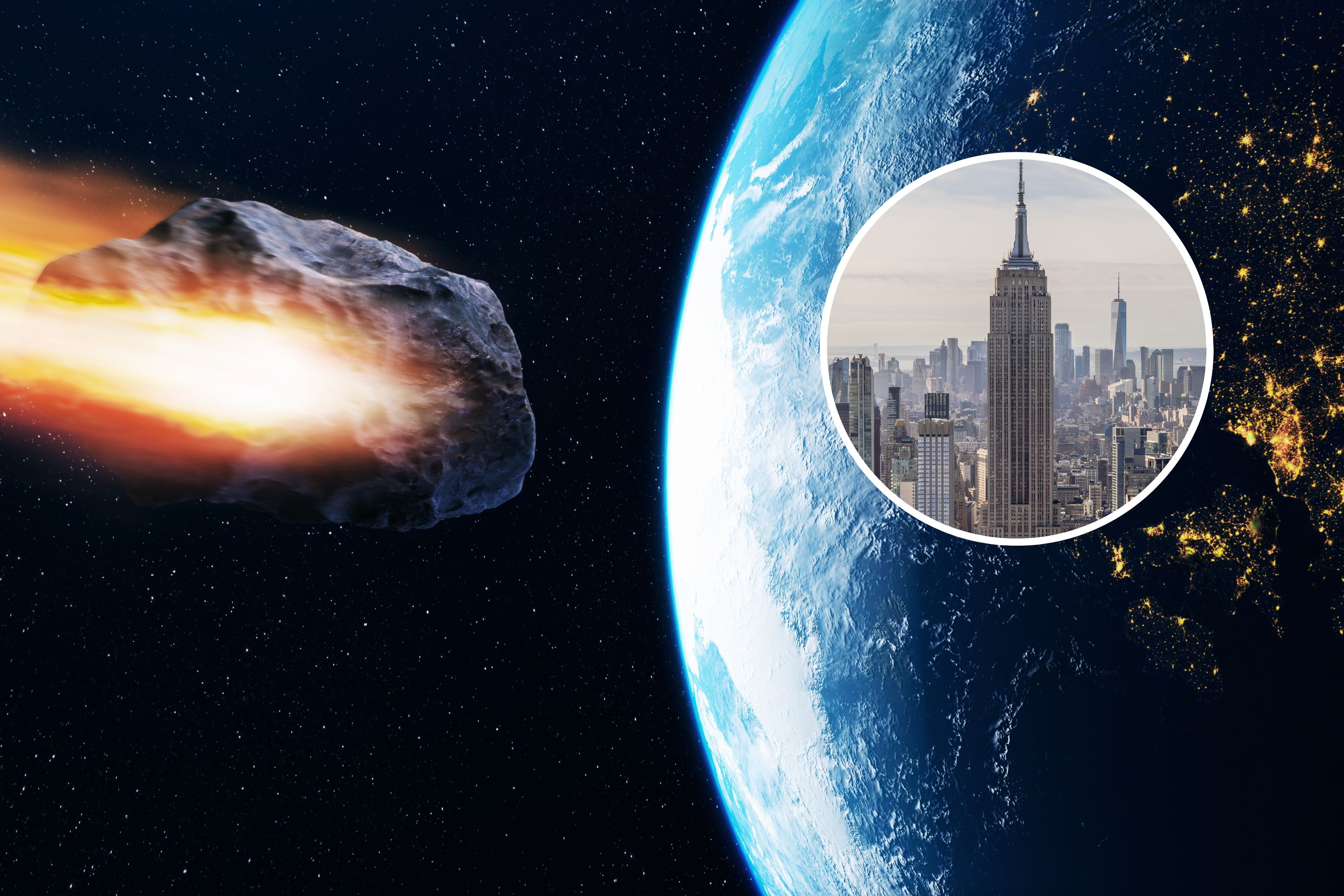
Empire State Building-sized
I linked, in my other comment, to the Tunguska Event, but the WP article happens to have an image showing the Empire State Building next to the Tunguska Event impactor (as well as the Chelyabinsk one) and I just had to highlight that, because the Tunguska impactor is much smaller.

The Tunguska event was a large explosion of between 3 and 50 megatons[2] that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of 30 June 1908.[1][3] The explosion over the sparsely populated East Siberian taiga flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of 2,150 km² (830 sq mi) of forest, and eyewitness accounts suggest up to three people may have died.
The Tunguska event is the largest impact event on Earth in recorded history, though much larger impacts occurred in prehistoric times. An explosion of this magnitude would be capable of destroying a large metropolitan area.[10] The event has been depicted in numerous works of fiction. The equivalent Torino scale rating for the impactor is 8: a certain collision with local destruction.
Maybe we’ll be put out of our misery after all? ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
I’m ready TBH
The moon passes us by 16 times closer than this thing, and it has way more bearing on terrestrial life. To suppose otherwise would be lunacy.
To suppose otherwise would be lunacy.
nice moon pun
SOONER OR LATER, it was bound to happen. On 30 June 1908, Moscow escaped destruction by three hours and four thousand kilometres—a margin invisibly small by the standards of the universe. Again, on 12 February 1947, yet another Russian city had a still narrower escape, when the second great meteorite of the twentieth century detonated less than four hundred kilometres from Vladivostok, with an explosion rivalling that of the newly invented uranium bomb.
In those days, there was nothing that men could do to protect themselves against the last random shots in the cosmic bombardment that had once scarred the face of the Moon. The meteorites of 1908 and 1947 had struck uninhabited wilderness; but by the end of the twenty-first century, there was no region left on Earth that could be safely used for celestial target practice. The human race had spread from pole to pole. And so, inevitably…
At 09.46 GMT on the morning of 11 September, in the exceptionally beautiful summer of the year 2077, most of the inhabitants of Europe saw a dazzling fireball appear in the eastern sky. Within seconds it was brighter than the sun, and as it moved across the heavens—at first in utter silence—it left behind it a churning column of dust and smoke.
Somewhere above Austria it began to disintegrate, producing a series of concussions so violent that more than a million people had their hearing permanently damaged. They were the lucky ones.
Moving at fifty kilometres a second, a thousand tons of rock and metal impacted on the plains of northern Italy, destroying in a few flaming moments the labour of centuries. The cities of Padua and Verona were wiped from the face of the earth; and the last glories of Venice sank for ever beneath the sea as the waters of the Adriatic came—thundering landwards after the hammer-blow from space.
Six hundred thousand people died, and the total damage was more than a trillion dollars. But the loss to art, to history, to science—to the whole human race, for the rest of time—was beyond all computation. It was as if a great war had been fought and lost in a single morning; and few could draw much pleasure from the fact that, as the dust of destruction slowly settled, for months the whole world witnessed the most splendid dawns and sunsets since Krakatoa.
After the initial shock, mankind reacted with a determination and a unity that no earlier age could have shown. Such a disaster, it was realized, might not occur again for a thousand years—but it might occur tomorrow. And the next time, the consequences could be even worse.
Very well; there would be no next time.
A hundred years earlier a much poorer world, with far feebler resources, had squandered its wealth attempting to destroy weapons launched, suicidally, by mankind against itself. The effort had never been successful, but the skills acquired then had not been forgotten. Now they could be used for a far nobler purpose, and on an infinitely vaster stage. No meteorite large enough to cause catastrophe would ever again be allowed to breach the defences of Earth.
So began Project SPACEGUARD. Fifty years later—and in a way that none of its designers could ever have anticipated—it justified its existence.
That’s the opening text of Arthur C. Clarke’s Rendevous with Rama. When it was published in 1973, it was science fiction speculating about the future. Today, we’re doing it – and on a much faster schedule than Clarke had envisioned. That’s kinda cool.
https://science.nasa.gov/planetary-defense/
Planetary Defense at NASA
https://phys.org/news/2021-11-nasa-deflect-asteroid-planetary-defense.html
NASA to deflect asteroid in test of ‘planetary defense’
I absolutely LOVED the first two books. Kinda fell apart after that.
Perfect, our chaos world will allow the later chapters to seem like masterpieces at this rate
The first book was pure Clarke, and one of my favorites of all time.
The last three were Clarke and gentry Lee. They were ok, but Lee tried to focus too much on characters, and Clarke does a better job at world building.
deleted by creator