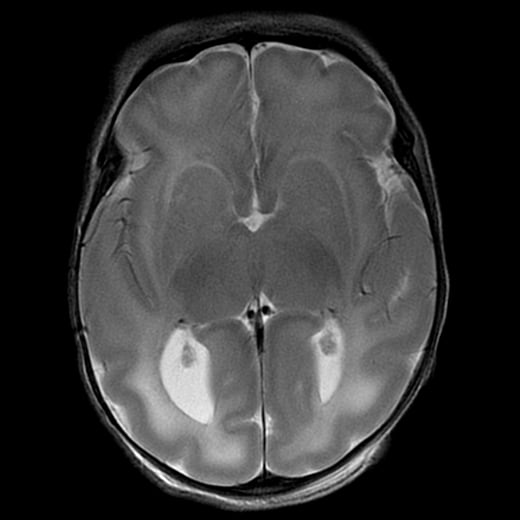
[LEFT]: This patient had one of the longer cerebellar tonsillar herniations I’ve seen. The tonsil is peg-like in shape and extends quite far below the foramen magnum to the level of the C2 posterior arch. As a result, there is crowding at the foramen magnum that is enough to impede CSF flow, resulting in hydrocephalus with dilated ventricles. Partly seen in the cervical cord from C2 and below is a syrinx, an associated finding. Chiari I is thought to be due to not enough space provided for the cerebellum by the calvarium or skull base shape, causing it to herniate into the spinal canal and cause trouble.
[RIGHT]: A comparison normal from online for you to compare the cerebellar tonsils.
I assume this is also causing the seemingly enlarged fourth ventricle?
Also, what are the treatment options? Do you have to drain this, or are there less inside remedies?
Yeah they can decompress by removing part of the back of the skull so there’s more space.