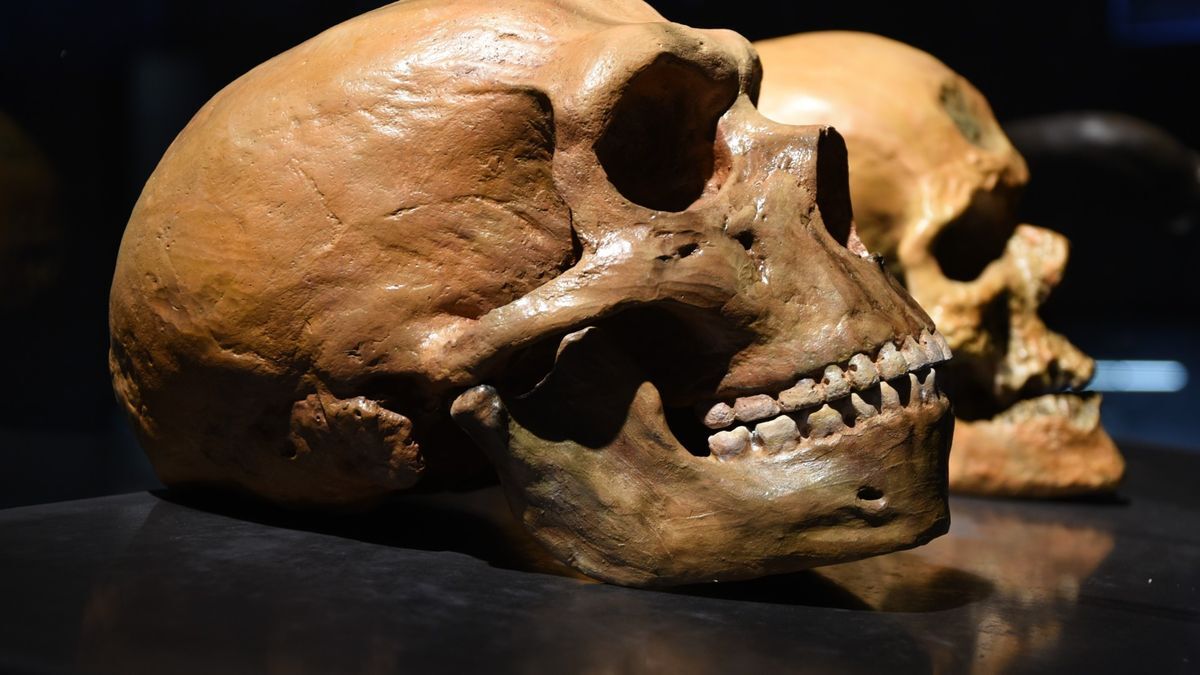
Neanderthals, which disappeared from the archaeological record roughly 40,000 years ago, have long been considered our closest evolutionary relatives. But almost since the first discovery of Neanderthal remains in the 1800s, scientists have been arguing over whether Neanderthals constitute their own species or if they’re simply a subset of our own species, Homo sapiens, that has since gone extinct.
So what does the science say? In particular, what does the genetic evidence, which didn’t exist back when many early hominins were first discovered, show?
You must log in or # to comment.