- cross-posted to:
- technology
- cross-posted to:
- technology
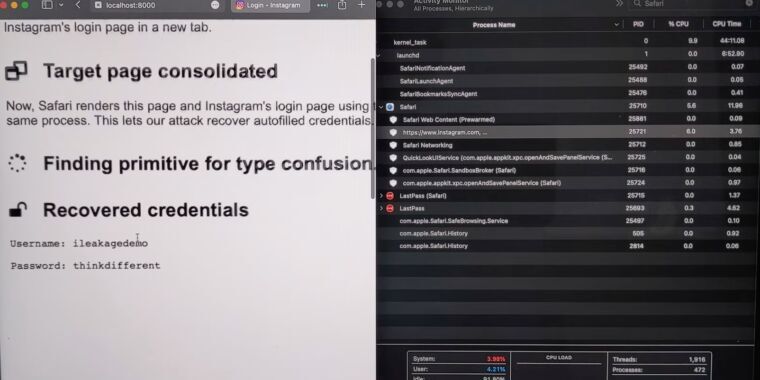
Researchers have devised an attack that forces Apple’s Safari browser to divulge passwords, Gmail message content, and other secrets by exploiting a side channel vulnerability in the A- and M-series CPUs running modern iOS and macOS devices.
iLeakage, as the academic researchers have named the attack, is practical and requires minimal resources to carry out. It does, however, require extensive reverse-engineering of Apple hardware and significant expertise in exploiting a class of vulnerability known as a side channel, which leaks secrets based on clues left in electromagnetic emanations, data caches, or other manifestations of a targeted system. The side channel in this case is speculative execution, a performance enhancement feature found in modern CPUs that has formed the basis of a wide corpus of attacks in recent years. The nearly endless stream of exploit variants has left chip makers—primarily Intel and, to a lesser extent, AMD—scrambling to devise mitigations.
. . .


From someone who works regularly with vulnerability management, it’s actually needed.
Vulnerabilities have really boring numbers and it’s difficult for humans to discuss them in a meaningful way. I believe the first vulnerability to get a “name” was heartbleed, the theory being that with a name people would take it seriously and discuss it properly. Given the severity of this vulnerability, it probably got a name but since it’s being patched by the vendors affected, it was probably not needed.
Heartbleed was needed because individual web sites had to update their software immediately or have their traffic intercepted.
Yeah, I hear you, fair point. I can’t recall CVE numbers off the top of my head either.
Heartbleed was also a great name, whereas iLeakage is… a choice.
I’ll probably be referring to it as ‘the latest Safari security failure’, hopefully they can ensure that description stays relevant for a few weeks.