The article is very misleading. It says
The research paper…notes that the human body is particularly efficient at generating 40 MHz RF energy. Tapping into that through a ‘worn receiver’ provides power without using any invasive means.
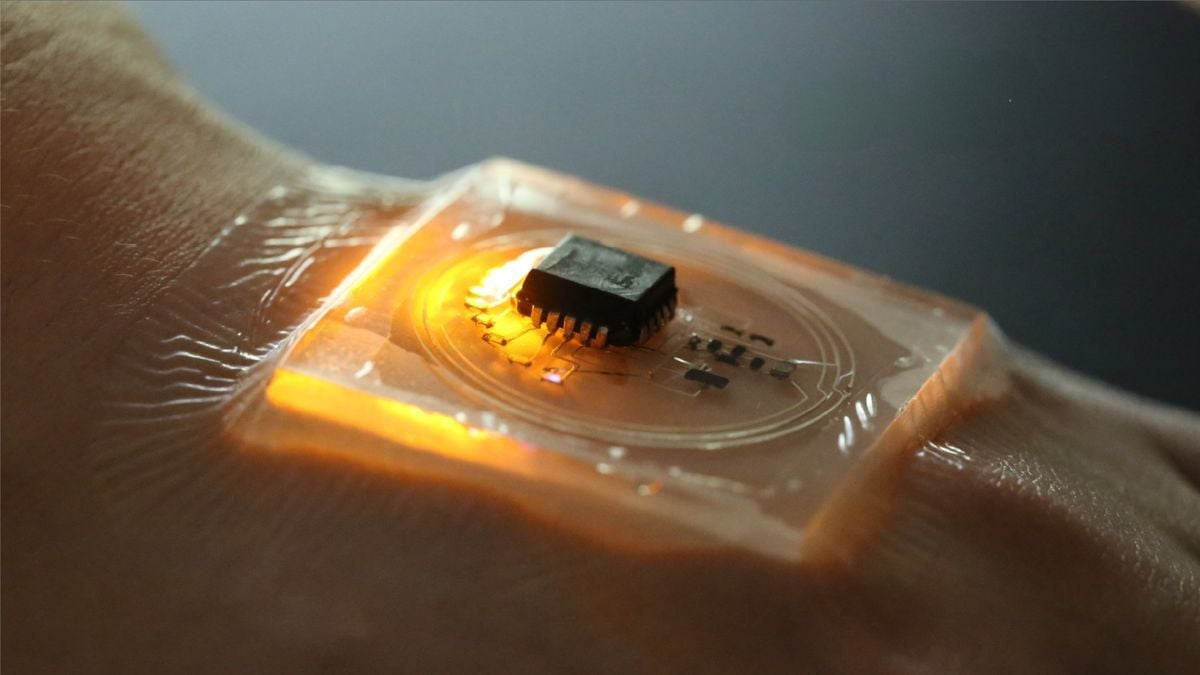
But I read much of the pdf linked at the bottom of that link, and there’s nothing about the human body generating energy at 40MHz. The trick is that skin is pretty effective (sort of) at conducting energy at that frequency, so the authors hooked up a power transmitter worn on the forearm, 5 or 15cm away from a receiver on the hand.
This isn’t about powering anything by body energy, it’s about strapping a battery-powered transmitter somewhere on your body and then having another device pick it up when strapped somewhere else on your body. No thanks.
Oh and it’s actually pretty inefficient and won’t provide much usable energy.
Off to spread
5G40MHz conspiracy theories.I was hoping they were talking about improvements in kinetic energy capture, like Seiko’s Kinetic line, which can power more demanding watches.
Is it only through the skin? I could see it being useful for some sort of implanted medical device/monitoring system.
That way you have something subcutaneous but the power source is strapped to the outside of your body so you can remove for short periods of time to wash/recharge it.
Seems it’s a re-write of this article from Monday, leaving out the transmitter part.
https://hackaday.com/2024/11/04/power-over-skin-makes-powering-wearables-easier/
(their source from 3 weeks ago) https://youtu.be/5PEN04-jyCU?si=JzzeLW6KalDKxOss
Power isn’t harvested from the human body it’s transmitted (in really small amounts) across the body from one device to another, using capacitive coupling and 40MHz AC voltage.
Tom’s hardware is declining in quality steadily. Suggesting VR and phones is a joke based on a 2mW budget. Yes you can do computation but not what a layman thinks it would do based on the examples they give.
Agreed. I wish the source page had a better summary of the research paper.
Power demand would have to drop significantly for that idea to work. I don’t think semiconductors are even capable of delivering enough computation with only 2 mW. Maybe a completely different sort of technology could pull it off, but currently there’s nothing like that in the horizon, so who knows if we’ll ever get human powered devices. Maybe some tiny computers with hardly any processing power could be a realistic application.
The article writer’s didn’t even read the paper they are reporting…
This is power-over-skin. Ie: power transmitted from one device to another via human skin. It’s not harvesting or generating energy from the human body.
The research paper, published by Andy Kong, Daehwa Kim, and Chris Harrison from Carnegie Mellon University, notes that the human body is particularly efficient at generating 40 MHz RF energy.
No. It doesn’t. At all…
Page 1 of the research paper PDF:
We call our technique Power-over-Skin Prior work has found that the human body is particularly efficient at conducting 40 MHz RF, while largely confining transmitted power to the body
Wasn’t machines using humans as batteries a plot point in the matrix? Why are people trying so hard to make these sci-fi nightmares a thing? 😆
There is a reason the “forbidden fruit” concept was chosen for inclusion in religious texts. :)