Day 11: Plutonian Pebbles
Megathread guidelines
- Keep top level comments as only solutions, if you want to say something other than a solution put it in a new post. (replies to comments can be whatever)
- You can send code in code blocks by using three backticks, the code, and then three backticks or use something such as https://topaz.github.io/paste/ if you prefer sending it through a URL
FAQ
- What is this?: Here is a post with a large amount of details: https://programming.dev/post/6637268
- Where do I participate?: https://adventofcode.com/
- Is there a leaderboard for the community?: We have a programming.dev leaderboard with the info on how to join in this post: https://programming.dev/post/6631465
Zee
Zee is my Dutch dialect of C. Since Dutch has compound words, so does Zee: “const char **” becomes vasteletterverwijzingsverwijzing, not vaste letter verwijzing verwijzing, which would be incorrect. A pointer to a long long unsigned int is, obviously, a zeergrootnatuurlijkgetalverwijzing.
Code
#ingesloten "zee.kop" #ingesloten "algemeen.kop" besloten getal splits( zeer groot natuurlijk getal x, zeergrootnatuurlijkgetalverwijzing a, zeergrootnatuurlijkgetalverwijzing b) { zeer groot natuurlijk getal m; getal n, g; mits (!x) lever 0; voor (n=0, m=1; m<=x; n++, m*=10) ; mits (n%2) lever 0; voor (g=0, m=1; g<n/2; g++, m*=10) ; volg a = x/m; volg b = x%m; lever 1; } #definieer GEHL (1024*1024) besloten zeer groot natuurlijk getal geh[GEHL][76]; besloten zeer groot natuurlijk getal afdalen(zeer groot natuurlijk getal w, getal n) { zeer groot natuurlijk getal a,b; mits (n<1 ) lever 1; mits (w==0) lever afdalen(1, n-1); mits (w<10) lever afdalen(w*2024, n-1); mits (w<GEHL && geh[w][n]) lever geh[w][n]; mits (!splits(w, naar a, naar b)) lever afdalen(w*2024, n-1); lever w<GEHL ? geh[w][n] = afdalen(a, n-1) + afdalen(b, n-1) : afdalen(a, n-1) + afdalen(b, n-1); } getal aanvang(getal parametersom, vasteletterverwijzingsverwijzing parameters) { zeer groot natuurlijk getal d1=0,d2=0, waarde; mits (parametersom > 1) VERWERP(heropen(parameters[1], "r", standaardinvoer)); zolang (invorm(" %llu", &waarde) == 1) { d1 += afdalen(waarde, 25); d2 += afdalen(waarde, 75); } uitvorm("11: %llu %llu\n", d1, d2); lever 0; }And of course we don’t have a Makefile but a Maakbestand:
alles: €{DAGEN} schoon: €{WIS} -f €{DAGEN} *.o ... .TWIJFELACHTIG: alles schoon oplossingen .UITGANGEN: .zee .o .zee.o: €{ZEE} €{VOORWERKVLAG} €{ZEEVLAG} -o €@ -c €<Yet more proof that the dutch are mad :D
Is it your own esolang, or is it commonly used by dutch speakers?
No it’s just me messing about with macros (but it does work!)
I do want to explore the type naming rules, see if I can write a parser for it. The C rules are funky by themselves but this is another level. “vaste letterverwijzing” is “char * const” but “vasteletterverwijzing” (without the space) is “const char *”. Then there’s grammatical gender: “vast getal” (const int) but “vaste letter” (const char)
Uiua
I thought this was going to be trivial to implement in Uiua, but I managed to blow the stack, meaning I had to set an environment variable in order to get it to run. That doesn’t work in Uiua Pad, so for any counts larger than 15 you need to run it locally. Built-in memoisation though so that’s nice.
# NB Needs env var UIUA_RECURSION_LIMIT=300 Next ← ⍣([1] °0|[×2024] °1◿2⧻°⋕.|⍜°⋕(↯2_∞)) Count ← |2 memo(⨬(1|/+≡Count¤-1⊙Next)≠0.) # rounds, stone ≡(&p/+≡Count¤: ⊜⋕⊸≠@\s "125 17")[25 75]Python
Part 1: ~2 milliseconds, Part 2: ~32 milliseconds, Total Time: ~32 milliseconds
You end up doing part 1 at the same time as part 2 but because of how Advent of Code works, you need to rerun the code after part 1 is solved. so Part 2 is technically total time.Fast Code
from time import perf_counter_ns transform_cache = {'0': [ '1']} def transform(current_stone): if len(current_stone) % 2 == 0: mid = len(current_stone) // 2 res = [current_stone[:mid], current_stone[mid:].lstrip('0').rjust(1,'0')] else: res = [str(int(current_stone) * 2024)] transform_cache[current_stone] = res return res def main(initial_stones): stones_count = {} for stone in initial_stones.split(): stones_count[stone] = stones_count.get(stone, 0) + 1 part1 = 0 for i in range(75): new_stones_count = {} for stone, count in stones_count.items(): for r in (transform_cache.get(stone) if stone in transform_cache else transform(stone)): new_stones_count[r] = new_stones_count.get(r, 0) + count stones_count = new_stones_count if i == 24: part1 = sum(stones_count.values()) return part1,sum(stones_count.values()) if __name__ == "__main__": with open('input', 'r') as f: input_data = f.read().replace('\r', '').replace('\n', '') start_time, part_one, part_two = perf_counter_ns(),*main(input_data) stop_time = perf_counter_ns() - start_time time_len = min(9, ((len(str(stop_time))-1)//3)*3) time_conversion = {9: 'seconds', 6: 'milliseconds', 3: 'microseconds', 0: 'nanoseconds'} print(f"Part 1: {part_one}\nPart 2: {part_two}\nProcessing Time: {stop_time / (10**time_len)} {time_conversion[time_len]}")Stepping through this code is what made it click for me, thanks. I was really mentally locked in on “memoizing” of the transform function, instead of realizing that the transform function only needs to be applied once per stone value.
Yours is still a lot faster than my rust version, so i’ll have to work out what is happening there.
Learning to profile code gives you a chance to learn what is inefficient code! I definitely like to spend sometime looking at it but at the end of the day. I really need to learn more languages. for now, I am sticking with trusty python. image bellow is in microseconds.
screenshots
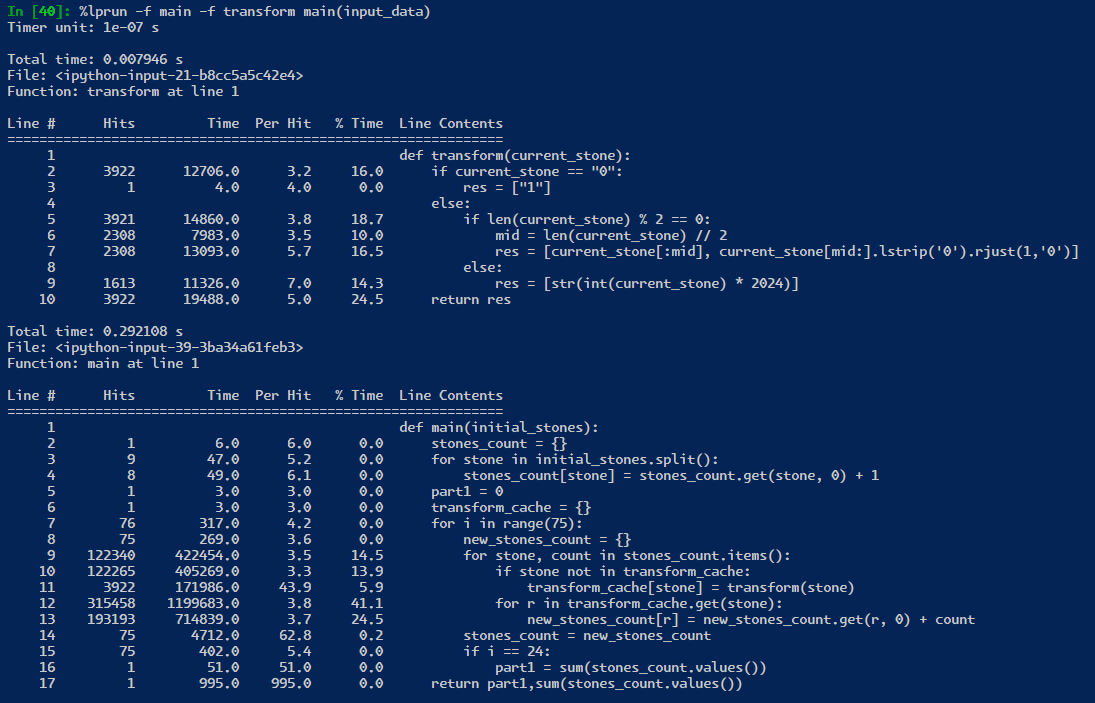
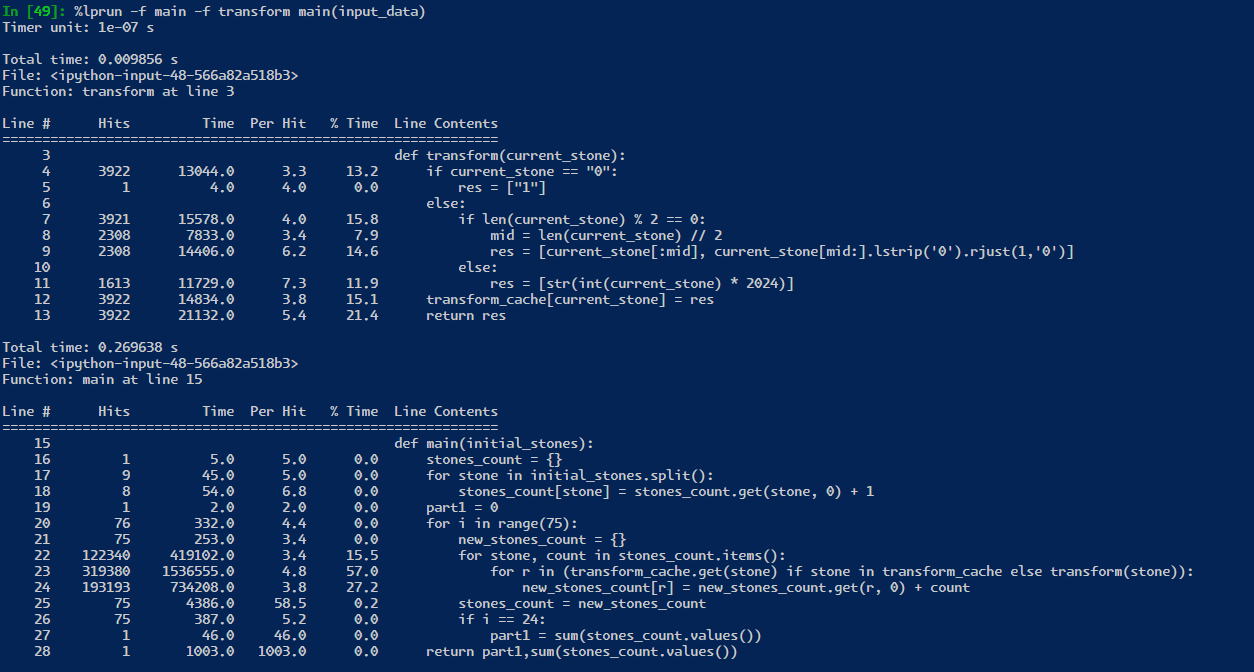
if the python process was kept alive, then we only are saving 25 milliseconds from ~250 to ~235! However, in real world testing, it seems that the profiler is not really a proper enough test! likely because the profiler is adding some overhead to each line of code.
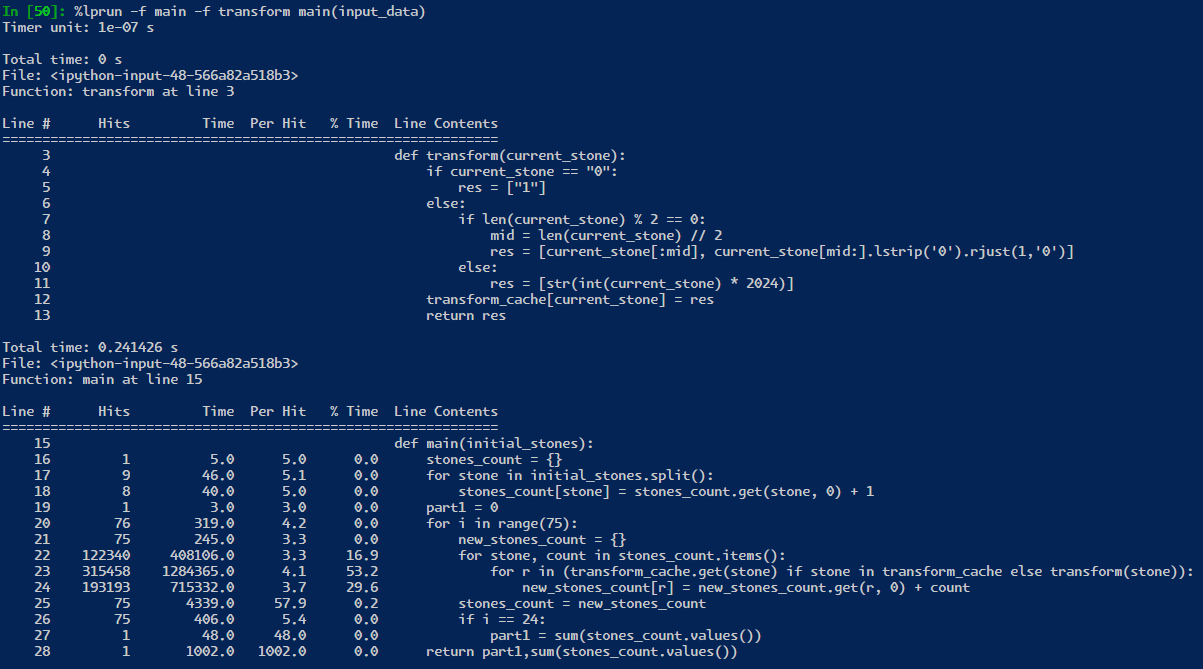
notice here, if I add this line of code:
transform_cache = {} BASE_DIR = dirname(realpath(__file__)) if isfile(join(BASE_DIR, r'transform_cache')): with open('transform_cache', 'r') as f: transform_cache = literal_eval(f.read().replace('\r','').replace('\n','')) transform_cache = {} # this makes the code faster???Notice I load from file a transform_cache from a previous run. However because of the “if stone in transform_cache” check, the loaded transform_cache is for some reason slower than allowing it to be filled up again. however, loading it and clearing it, is faster because the cpu/ram/OS is probably doing their own caching, too. if we remove the “if stone in transform_cache” check and keep the transform_cache fully loaded, then it is faster by ~1 millisecond, down to 29 milliseconds! these are the niche problems with caching things and squeezing all the performance out of code.
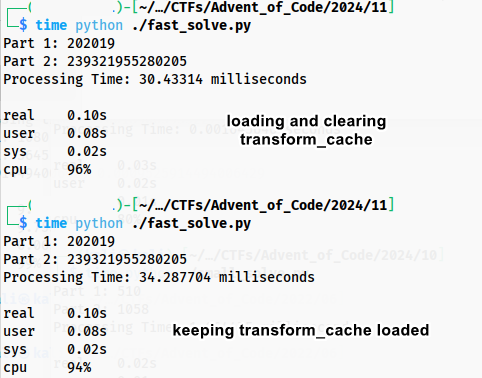
Yeah, I have been using these slow challenges to improve my profiling ability. It is a bit of a dark art though, especially with compiled languages.
My slowest part seems to be the hashmap, but there isnt much I can do about that I think.
Also, if I do a release run I can get 10ms, but that feels like cheating :D
Hey that is what release mode is for! optimizing by unrolling and other tricks is needed, but in your case, I think I remember someone mention their rust release mode is closer to 2 ms.
I did try something like PyPy3 but it seems to be slower by ~3 milliseconds! So I don’t know where I could improve my code any further without unrolling the range(75) loop. though would only make it closer to ~29 ms on avg.
Edit: apparently they updated their code to be closer to 250 micro seconds. that is blazing fast [ link ]
Using release to beat python code is just a very hollow victory :D
It does somewhat depend on how we measure as well, you are benching the algorithm itself, and I’m doing the entire execution time
you are right, I dont think loading the file from disk should be part of it because OS process priority/queue, disk and cache and more headaches on figuring out what is slow. If you want to compare the entire execution including python startup overhead and reading from file and anything extra. it is closer 50 to 60 ms on linux and 80-90 ms on windows. (both hosts, not virtual machines)
My reasoning is that loading the input will eventually either pull from the website or disk. that is not part of the challenge. you could simply just hard code it.
So maybe you should look into adding code to your debug mode or both modes for measuring solving it instead of the entire process loading.
however, someone claims their rust code can do 250 microseconds, so I doubt you have much excuse aside from having “inefficient” code.(you are still fast, just not at the limit of your Language’s performance) only measuring my python algorithm, it is only able to finish in 32000 microseconds.
https://github.com/maneatingape/advent-of-code-rust/blob/main/src/year2024/day11.rs
however, now that I am looking at their
main.rsfile, they do calculate time for completion after process startup and only the algorithm.Yeah, disk loading definitely shouldn’t count if I was timing properly, I’m just lazy and dont want to do proper timing. :D
Most of my slowdown is in the hashmap, looks like that answer deconstructs the hashmap and builds it from a fastmap and a vec. Not sure I want to go down that road, at this stage.
Thanks again for your code and help :)
Haskell
import Data.Monoid import Control.Arrow data Tree v = Tree (Tree v) v (Tree v) -- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3208258 memo1 f = index nats where nats = go 0 1 go i s = Tree (go (i + s) s') (f i) (go (i + s') s') where s' = 2 * s index (Tree l v r) i | i < 0 = f i | i == 0 = v | otherwise = case (i - 1) `divMod` 2 of (i', 0) -> index l i' (i', 1) -> index r i' memo2 f = memo1 (memo1 . f) blink = memo2 blink' where blink' c n | c == 0 = 1 | n == 0 = blink c' 1 | even digits = blink c' l <> blink c' r | otherwise = blink c' $ n * 2024 where digits = succ . floor . logBase 10 . fromIntegral $ n (l, r) = n `divMod` (10 ^ (digits `div` 2)) c' = pred c doBlinks n = getSum . mconcat . fmap (blink n) part1 = doBlinks 25 part2 = doBlinks 75 main = getContents >>= print . (part1 &&& part2) . fmap read . wordsRust
Part 2 is solved with recursion and a cache, which is indexed by stone numbers and remaining rounds and maps to the previously calculated expansion size. In my case, the cache only grew to 139320 entries, which is quite reasonable given the size of the result.
Solution
use std::collections::HashMap; fn parse(input: String) -> Vec<u64> { input .split_whitespace() .map(|w| w.parse().unwrap()) .collect() } fn part1(input: String) { let mut stones = parse(input); for _ in 0..25 { let mut new_stones = Vec::with_capacity(stones.len()); for s in &stones { match s { 0 => new_stones.push(1), n => { let digits = s.ilog10() + 1; if digits % 2 == 0 { let cutoff = 10u64.pow(digits / 2); new_stones.push(n / cutoff); new_stones.push(n % cutoff); } else { new_stones.push(n * 2024) } } } } stones = new_stones; } println!("{}", stones.len()); } fn expansion(s: u64, rounds: u32, cache: &mut HashMap<(u64, u32), u64>) -> u64 { // Recursion anchor if rounds == 0 { return 1; } // Calculation is already cached if let Some(res) = cache.get(&(s, rounds)) { return *res; } // Recurse let res = match s { 0 => expansion(1, rounds - 1, cache), n => { let digits = s.ilog10() + 1; if digits % 2 == 0 { let cutoff = 10u64.pow(digits / 2); expansion(n / cutoff, rounds - 1, cache) + expansion(n % cutoff, rounds - 1, cache) } else { expansion(n * 2024, rounds - 1, cache) } } }; // Save in cache cache.insert((s, rounds), res); res } fn part2(input: String) { let stones = parse(input); let mut cache = HashMap::new(); let sum: u64 = stones.iter().map(|s| expansion(*s, 75, &mut cache)).sum(); println!("{sum}"); } util::aoc_main!();Also on github
And now we get into the days where caching really is king. My first attempt didn’t go so well, I tried to handle the full list result as one cache step, instead of individually caching the result of calculating each stone per step.
I think my original attempt is still calculating at home, but I finished up this much better version on the trip to work.
All hail public transport.C#
List<long> stones = new List<long>(); public void Input(IEnumerable<string> lines) { stones = string.Concat(lines).Split(' ').Select(v => long.Parse(v)).ToList(); } public void Part1() { var expanded = TryExpand(stones, 25); Console.WriteLine($"Stones: {expanded}"); } public void Part2() { var expanded = TryExpand(stones, 75); Console.WriteLine($"Stones: {expanded}"); } public long TryExpand(IEnumerable<long> stones, int steps) { if (steps == 0) return stones.Count(); return stones.Select(s => TryExpand(s, steps)).Sum(); } Dictionary<(long, int), long> cache = new Dictionary<(long, int), long>(); public long TryExpand(long stone, int steps) { var key = (stone, steps); if (cache.ContainsKey(key)) return cache[key]; var result = TryExpand(Blink(stone), steps - 1); cache[key] = result; return result; } public IEnumerable<long> Blink(long stone) { if (stone == 0) { yield return 1; yield break; } var str = stone.ToString(); if (str.Length % 2 == 0) { yield return long.Parse(str[..(str.Length / 2)]); yield return long.Parse(str[(str.Length / 2)..]); yield break; } yield return stone * 2024; }Nim
Runtime: 30-40 ms
I’m not very experienced with recursion and memoization, so this took me quite a while.Edit: slightly better version
template splitNum(numStr: string): seq[int] = @[parseInt(numStr[0..<numStr.len div 2]), parseInt(numStr[numStr.len div 2..^1])] template applyRule(stone: int): seq[int] = if stone == 0: @[1] else: let numStr = $stone if numStr.len mod 2 == 0: splitNum(numStr) else: @[stone * 2024] proc memRule(st: int): seq[int] = var memo {.global.}: Table[int, seq[int]] if st in memo: return memo[st] result = st.applyRule memo[st] = result proc countAfter(stone: int, targetBlinks: int): int = var memo {.global.}: Table[(int, int), int] if (stone,targetBlinks) in memo: return memo[(stone,targetBlinks)] if targetBlinks == 0: return 1 for st in memRule(stone): result += st.countAfter(targetBlinks - 1) memo[(stone,targetBlinks)] = result proc solve(input: string): AOCSolution[int, int] = for stone in input.split.map(parseInt): result.part1 += stone.countAfter(25) result.part2 += stone.countAfter(75)
Haskell
Yay, mutation! Went down the route of caching the expanded lists of stones at first. Oops.
import Data.IORef import Data.Map.Strict (Map) import Data.Map.Strict qualified as Map blink :: Int -> [Int] blink 0 = [1] blink n | s <- show n, l <- length s, even l = let (a, b) = splitAt (l `div` 2) s in map read [a, b] | otherwise = [n * 2024] countExpanded :: IORef (Map (Int, Int) Int) -> Int -> [Int] -> IO Int countExpanded _ 0 = return . length countExpanded cacheRef steps = fmap sum . mapM go where go n = let key = (n, steps) computed = do result <- countExpanded cacheRef (steps - 1) $ blink n modifyIORef' cacheRef (Map.insert key result) return result in readIORef cacheRef >>= maybe computed return . (Map.!? key) main = do input <- map read . words <$> readFile "input11" cache <- newIORef Map.empty mapM_ (\steps -> countExpanded cache steps input >>= print) [25, 75]Does the IORef go upwards the recursion tree? If you modify the IORef at some depth of 15, does the calling function also receive the update, is there also a Non-IO-Ref?
The IORef is like a mutable box you can stick things in, so
readIORefreturns whatever was last put in it (in this case usingmodifyIORef'). “last” makes sense here because operations are sequenced thanks to the IO monad, so yes: values get carried back up the tree to the caller. There’s alsoSTReffor the ST monad, or I could have used the State monad which (kind of) encapsulates a single ref.
Haskell
Sometimes I want something mutable, this one takes 0.3s, profiling tells me 30% of my time is spent creating new objects. :/
import Control.Arrow import Data.Map.Strict (Map) import qualified Data.Map.Strict as Map import qualified Data.Maybe as Maybe type StoneCache = Map Int Int type BlinkCache = Map Int StoneCache parse :: String -> [Int] parse = lines >>> head >>> words >>> map read memoizedCountSplitStones :: BlinkCache -> Int -> Int -> (Int, BlinkCache) memoizedCountSplitStones m 0 _ = (1, m) memoizedCountSplitStones m i n | Maybe.isJust maybeMemoized = (Maybe.fromJust maybeMemoized, m) | n == 0 = do let (r, rm) = memoizedCountSplitStones m (pred i) (succ n) let rm' = cacheWrite rm i n r (r, rm') | digitCount `mod` 2 == 0 = do let (r1, m1) = memoizedCountSplitStones m (pred i) firstSplit let (r2, m2) = memoizedCountSplitStones m1 (pred i) secondSplit let m' = cacheWrite m2 i n (r1+r2) (r1 + r2, m') | otherwise = do let (r, m') = memoizedCountSplitStones m (pred i) (n * 2024) let m'' = cacheWrite m' i n r (r, m'') where secondSplit = n `mod` (10 ^ (digitCount `div` 2)) firstSplit = (n - secondSplit) `div` (10 ^ (digitCount `div` 2)) digitCount = succ . floor . logBase 10 . fromIntegral $ n maybeMemoized = cacheLookup m i n foldMemoized :: Int -> (Int, BlinkCache) -> Int -> (Int, BlinkCache) foldMemoized i (r, m) n = (r + r2, m') where (r2, m') = memoizedCountSplitStones m i n cacheWrite :: BlinkCache -> Int -> Int -> Int -> BlinkCache cacheWrite bc i n r = Map.adjust (Map.insert n r) i bc cacheLookup :: BlinkCache -> Int -> Int -> Maybe Int cacheLookup bc i n = do sc <- bc Map.!? i sc Map.!? n emptyCache :: BlinkCache emptyCache = Map.fromList [ (i, Map.empty) | i <- [1..75]] part1 = foldl (foldMemoized 25) (0, emptyCache) >>> fst part2 = foldl (foldMemoized 75) (0, emptyCache) >>> fst main = getContents >>= print . (part1 &&& part2) . parseSome nice monadic code patterns going on there, passing the cache around! (You might want to look into the State monad if you haven’t come across it before)
Thank you for the hint, I wouldn’t have recognized it because I haven’t yet looked into it, I might try it this afternoon if I find the time, I could probably put both the Cache and the current stone count into the monad state?
Your code as it stands is basically
State BlinkCachewritten out explicitly, which is I think a natural way to structure the solution. That is, the cache is the state, and the stone count is the (monadic) return value. Good luck!
Dart
I really wish Dart had memoising built in. Maybe the new macro feature will allow this to happen, but in the meantime, here’s my hand-rolled solution.
import 'package:collection/collection.dart'; var counter_ = <(int, int), int>{}; int counter(s, [r = 75]) => counter_.putIfAbsent((s, r), () => _counter(s, r)); int _counter(int stone, rounds) => (rounds == 0) ? 1 : next(stone).map((e) => counter(e, rounds - 1)).sum; List<int> next(int s) { var ss = s.toString(), sl = ss.length; if (s == 0) return [1]; if (sl.isOdd) return [s * 2024]; return [ss.substring(0, sl ~/ 2), ss.substring(sl ~/ 2)] .map(int.parse) .toList(); } solve(List<String> lines) => lines.first.split(' ').map(int.parse).map(counter).sum;C#
public class Day11 : Solver { private long[] data; private class TreeNode(TreeNode? left, TreeNode? right, long value) { public TreeNode? Left = left; public TreeNode? Right = right; public long Value = value; } private Dictionary<(long, int), long> generation_length_cache = []; private Dictionary<long, TreeNode> subtree_pointers = []; public void Presolve(string input) { data = input.Trim().Split(" ").Select(long.Parse).ToArray(); List<TreeNode> roots = data.Select(value => new TreeNode(null, null, value)).ToList(); List<TreeNode> last_level = roots; subtree_pointers = roots.GroupBy(root => root.Value) .ToDictionary(grouping => grouping.Key, grouping => grouping.First()); for (int i = 0; i < 75; i++) { List<TreeNode> next_level = []; foreach (var node in last_level) { long[] children = Transform(node.Value).ToArray(); node.Left = new TreeNode(null, null, children[0]); if (subtree_pointers.TryAdd(node.Left.Value, node.Left)) { next_level.Add(node.Left); } if (children.Length <= 1) continue; node.Right = new TreeNode(null, null, children[1]); if (subtree_pointers.TryAdd(node.Right.Value, node.Right)) { next_level.Add(node.Right); } } last_level = next_level; } } public string SolveFirst() => data.Select(value => GetGenerationLength(value, 25)).Sum().ToString(); public string SolveSecond() => data.Select(value => GetGenerationLength(value, 75)).Sum().ToString(); private long GetGenerationLength(long value, int generation) { if (generation == 0) { return 1; } if (generation_length_cache.TryGetValue((value, generation), out var result)) return result; TreeNode cur = subtree_pointers[value]; long sum = GetGenerationLength(cur.Left.Value, generation - 1); if (cur.Right is not null) { sum += GetGenerationLength(cur.Right.Value, generation - 1); } generation_length_cache[(value, generation)] = sum; return sum; } private IEnumerable<long> Transform(long arg) { if (arg == 0) return [1]; if (arg.ToString() is { Length: var l } str && (l % 2) == 0) { return [int.Parse(str[..(l / 2)]), int.Parse(str[(l / 2)..])]; } return [arg * 2024]; } }I had a very similar take on this problem, but I was not caching the results of a blink for a single stone, like youre doing with
subtree_pointers. I tried adding that to my solution, but it didn’t make an appreciable difference. I think that caching the lengths is really the only thing that matters.C#
static object Solve(Input i, int numBlinks) { // This is a cache of the tuples of (stoneValue, blinks) to // the calculated count of their child stones. var lengthCache = new Dictionary<(long, int), long>(); return i.InitialStones .Sum(stone => CalculateUltimateLength(stone, numBlinks, lengthCache)); } static long CalculateUltimateLength( long stone, int numBlinks, IDictionary<(long, int), long> lengthCache) { if (numBlinks == 0) return 1; if (lengthCache.TryGetValue((stone, numBlinks), out var length)) return length; length = Blink(stone) .Sum(next => CalculateUltimateLength(next, numBlinks - 1, lengthCache)); lengthCache[(stone, numBlinks)] = length; return length; } static long[] Blink(long stone) { if (stone == 0) return [1]; var stoneText = stone.ToString(); if (stoneText.Length % 2 == 0) { var halfLength = stoneText.Length / 2; return [ long.Parse(stoneText.Substring(0, halfLength)), long.Parse(stoneText.Substring(halfLength)), ]; } return [stone * 2024]; }I think that caching the lengths is really the only thing that matters.
Yep, it is just a dynamic programming problem really.
Python
I initially cached the calculate_next function but honestly number of unique numbers don’t grow that much (couple thousands) so I did not feel a difference when I removed the cache. Using a dict just blazes through the problem.
from pathlib import Path from collections import defaultdict cwd = Path(__file__).parent def parse_input(file_path): with file_path.open("r") as fp: numbers = list(map(int, fp.read().splitlines()[0].split(' '))) return numbers def calculate_next(val): if val == 0: return [1] if (l:=len(str(val)))%2==0: return [int(str(val)[:int(l/2)]), int(str(val)[int(l/2):])] else: return [2024*val] def solve_problem(file_name, nblinks): numbers = parse_input(Path(cwd, file_name)) nvals = 0 for indt, node in enumerate(numbers): last_nodes = {node:1} counter = 0 while counter<nblinks: new_nodes = defaultdict(int) for val,count in last_nodes.items(): val_next_nodes = calculate_next(val) for node in val_next_nodes: new_nodes[node] += count last_nodes = new_nodes counter += 1 nvals += sum(last_nodes.values()) return nvalsKotlin
Gone mathematical.
Also overflowing indices screwed with me a bit.
Here's the code:
import kotlin.math.floor import kotlin.math.log import kotlin.math.pow import kotlin.time.DurationUnit fun main() { fun part1(input: List<String>): Long = Day11Solver(input).solve(25) fun part2(input: List<String>): Long = Day11Solver(input).solve(75) val testInput = readInput("Day11_test") check(part1(testInput) == 55312L) //check(part2(testInput) == 0L) No test output available. val input = readInput("Day11") part1(input).println() part2(input).println() timeTrials("Part 1", unit = DurationUnit.MICROSECONDS) { part1(input) } timeTrials("Part 2", repetitions = 1000) { part2(input) } } class Day11Solver(input: List<String>) { private val parsedInput = input[0].split(' ').map { it.toLong() } /* * i ∈ ℕ₀ ∪ {-1}, φᵢ: ℕ₀ → ℕ shall be the function mapping the amount of stones generated to the amount of steps * taken with a stone of starting number i. * * Furthermore, ѱ: ℕ₀ → ℕ₀ ⨯ (ℕ₀ ∪ {-1}) shall be the function mapping an index to two new indices after a step. * * ⎧ (1, -1) if i = 0 * ѱ(i) := ⎨ (a, b) if ⌊lg(i)⌋ + 1 ∈ 2 ℕ with a := i/(10^((⌊lg(i)⌋ + 1) / 2)), b := i - 10^((⌊lg(i)⌋ + 1) / 2) * a * ⎩ (2024 i, -1) otherwise * * ⎧ 0 if i = -1 * φᵢ(n) := ⎨ 1 if n = 0 * ⎩ φₖ(n - 1) + φₗ(n - 1) otherwise with (k, l) := ѱ(i) * * With that φᵢ(n) is a sum with n up to 2ⁿ summands, that are either 0 or 1. */ private val cacheIndices = mutableMapOf<Long, Pair<Long, Long>>() // Cache the next indices for going from φᵢ(n) to φₖ(n - 1) + φₗ(n - 1). private val cacheValues = mutableMapOf<Pair<Long, Int>, Long>() // Also cache already calculated φᵢ(n) fun calculatePsi(i: Long): Pair<Long, Long> = cacheIndices.getOrPut(i) { if(i == -1L) throw IllegalArgumentException("Advancement made: How did we get here?") else if (i == 0L) 1L to -1L else { val amountOfDigits = (floor(log(i.toDouble(), 10.0)) + 1) if (amountOfDigits.toLong() % 2 == 0L) { // Split digits at the midpoint. val a = floor(i / 10.0.pow(amountOfDigits / 2)) val b = i - a * 10.0.pow(amountOfDigits / 2) a.toLong() to b.toLong() } else { 2024 * i to -1L } } } fun calculatePhi(i: Long, n: Int): Long = cacheValues.getOrPut(i to n) { if (i == -1L) 0L else if (n == 0) 1L else { val (k, l) = calculatePsi(i) calculatePhi(k, n - 1) + calculatePhi(l, n - 1) } } fun solve(steps: Int): Long = parsedInput.sumOf { val debug = calculatePhi(it, steps) debug } }
Try it out here.
And this is the full repo.
C
Started out a bit sad that this problem really seemed to call for hash tables - either for storing counts for an iterative approach, or to memoize a recursive one.
Worried that the iterative approach would have me doing problematic O(n^2) array scans I went with recursion and a plan to memoize only the first N integers in a flat array, expecting low integers to be much more frequent (and dense) than higher ones.
After making an embarrassing amount of mistakes it worked out beautifully with N=1m (testing revealed that to be about optimal). Also applied some tail recursion shortcuts where possible.
day11 0:00.01 6660 Kb 0+1925 faultsCode
#include "common.h" /* returns 1 and splits x if even-digited, 0 otherwise */ static int split(uint64_t x, uint64_t *a, uint64_t *b) { uint64_t p; int n, i; if (!x) return 0; for (n=0, p=1; p<=x; n++, p*=10) ; if (n%2) return 0; for (i=0, p=1; i<n/2; i++, p*=10) ; *a = x/p; *b = x%p; return 1; } /* * recur() is memoized in mem[]. Testing found the size MEMZ to be optimal: * lowering siginificantly reduced hits, but raising tenfold didn't add a * single hit. */ #define MEMZ (1024*1024) static uint64_t mem[MEMZ][76]; static uint64_t recur(uint64_t v, int n) { uint64_t a,b; if (n<1 ) return 1; if (v==0) return recur(1, n-1); if (v<10) return recur(v*2024, n-1); if (v<MEMZ && mem[v][n]) return mem[v][n]; if (!split(v, &a, &b)) return recur(v*2024, n-1); return v<MEMZ ? mem[v][n] = recur(a, n-1) + recur(b, n-1) : recur(a, n-1) + recur(b, n-1); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { uint64_t p1=0,p2=0, val; if (argc > 1) DISCARD(freopen(argv[1], "r", stdin)); while (scanf(" %"SCNu64, &val) == 1) { p1 += recur(val, 25); p2 += recur(val, 75); } printf("10: %"PRId64" %"PRId64"\n", p1, p2); return 0; }








